7569번: 토마토
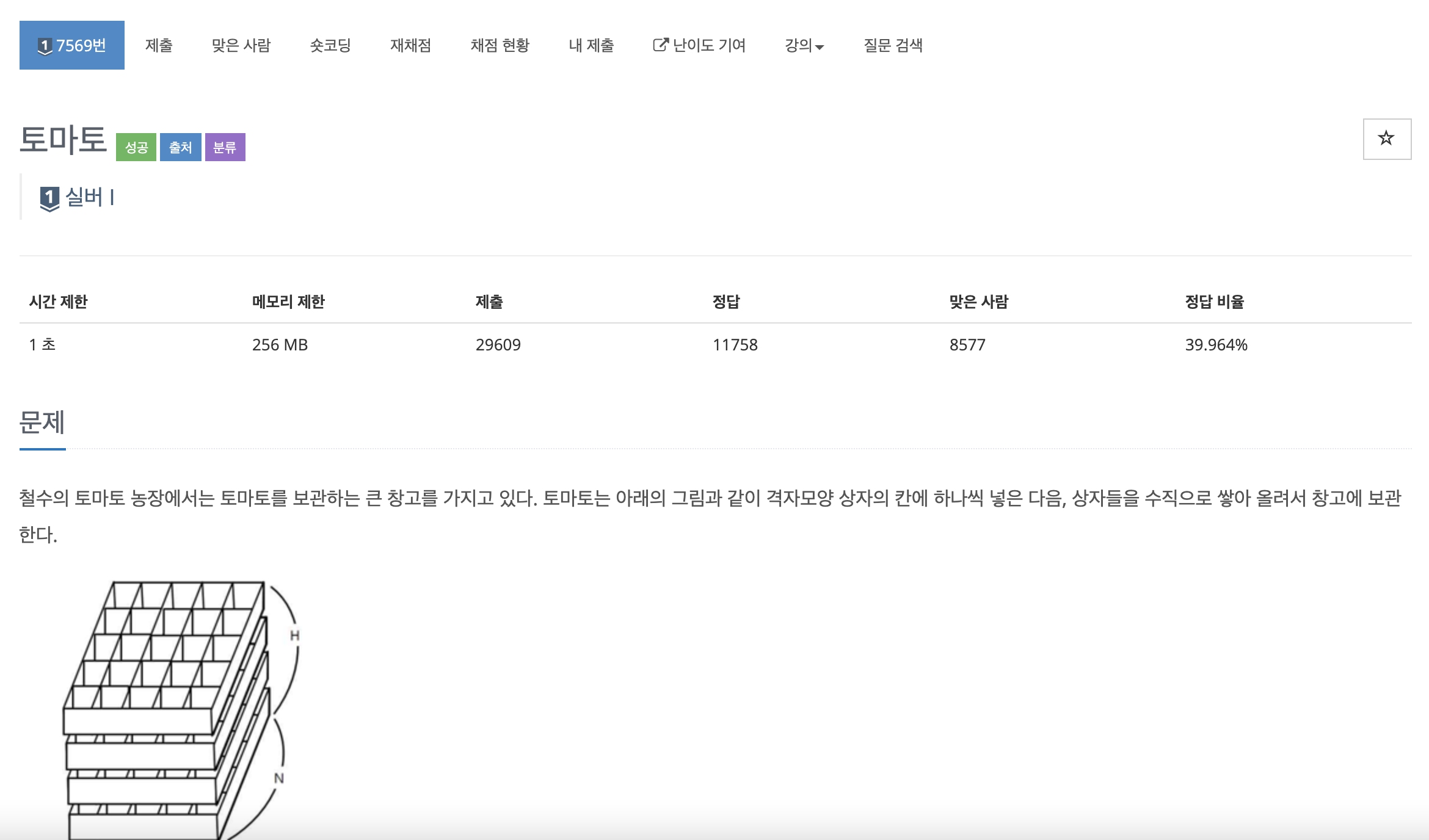
첫 줄에는 상자의 크기를 나타내는 두 정수 M,N과 쌓아올려지는 상자의 수를 나타내는 H가 주어진다. M은 상자의 가로 칸의 수, N은 상자의 세로 칸의 수를 나타낸다. 단, 2 ≤ M ≤ 100, 2 ≤ N ≤ 100,
www.acmicpc.net
C++ BFS
토마토 농장주가 된 기분이네요. 어제에 이어 오늘도 토마토를 익혔답니다.
다음문제가 토마토인것을 보자마자 소스라치게 놀랐어요. 하지만 어제 풀었던 거니까..하면서 풀었는데
다행히 3차원으로만 늘리는 설정만 하면 되는 코드였어요.
접근방법
2차원 토마토 문제에서 3차원배열로 늘려주고, 인접 토마토 확인할 때에도 dh를 추가해서 위 아래 토마토를 확인할 수 있도록 고쳐준다.
소스코드
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n,m,h;
int map[105][105][105];
int visit[105][105][105];
int dr[6] = {0,0,1,-1,0,0};
int dc[6] = {1,-1,0,0,0,0};
int dh[6] = {0,0,0,0,1,-1};
bool isFull(){
for(int k = 0 ; k < h ; k++){
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(map[k][i][j] == 0){
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin >> m >> n >> h;
queue<vector<int>> q;
int input;
for(int k = 0 ; k < h ; k++){
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
cin >> input;
map[k][i][j] = input;
if(input == 1){
q.push({k,i,j});
}
}
}
}
int cnt = 0;
if(isFull()){
cout << cnt;
return 0;
}
long pushcnt = q.size();
while(!q.empty()){
int hereH = q.front()[0];
int hereR = q.front()[1];
int hereC = q.front()[2];
q.pop();
pushcnt--;
visit[hereH][hereR][hereC] = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 6 ; i++){
int thereH = hereH + dh[i];
int thereR = hereR + dr[i];
int thereC = hereC + dc[i];
if(thereH >= 0 && thereH < h && thereR >= 0 && thereC >= 0 && thereR < n && thereC < m && map[thereH][thereR][thereC] == 0 && !visit[thereH][thereR][thereC]){
q.push({thereH,thereR,thereC});
map[thereH][thereR][thereC] = 1;
}
}
if(pushcnt == 0){
cnt++;
pushcnt = q.size();
}
}
cout << (isFull() ? cnt-1 : -1);
return 0;
}
728x90
'알고리즘 문제풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 7562] 알고리즘 88일차 : 나이트의 이동 (0) | 2021.02.19 |
|---|---|
| [백준 1697] 알고리즘 87일차 : 숨바꼭질 (0) | 2021.02.18 |
| [백준 7576] 알고리즘 85일차 : 토마토 (0) | 2021.02.16 |
| [백준 2178] 알고리즘 84일차 : 미로탐색 (0) | 2021.02.15 |
| [백준 1012] 알고리즘 83일차 : 유기농 배추 (0) | 2021.02.10 |



